In the context of the intensifying global new crown epidemic, vaccines are placed on high hopes to completely end the epidemic. In March, China and the United States announced that vaccine research entered the clinical stage almost at the same time, and now there are more than 100 new crown vaccine researches underway around the world.
Although the World Health Organization has emphasized more than once that the development of a vaccine will be difficult to complete within 18 months, many teams are still eager to make history. This article will take you through a look at the methods available to these teams, each of which exists What difficulties, and is there any way to make the arrival of the vaccine faster.
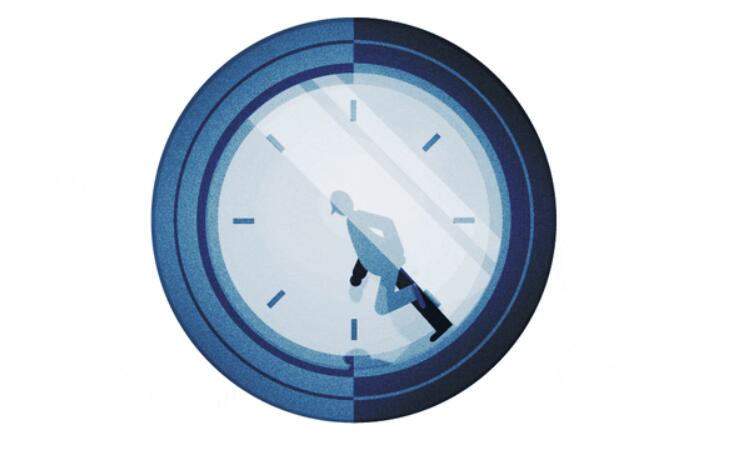

Different vaccine development routes have their own advantages and disadvantages
For the development of this new coronavirus vaccine, different research teams in many countries have different strategies, some of which are traditional and some are new.
Live attenuated vaccine to domesticate wild horses as mounts
We are not unfamiliar with this kind of vaccine. The sugar pill to prevent polio is a live attenuated vaccine. As the name suggests,Live vaccines refer to vaccines that use live viruses, but after Modified, less virulent, usually not pathogenic. It's like wild horses have been domesticated and become obedient mounts, but the running function is still there .
In addition to the live attenuated polio vaccine, measles, chickenpox, and the first Japanese encephalitis vaccine exported overseas with independent intellectual property rights are all live attenuated vaccines. The biggest advantage of live attenuated vaccines is that the effect of live virus infecting the human body is close to natural infection.Generally speaking, the immune effect is good and the immune response is fast. The cost of vaccine production is not high, and it is easy to mass-produce. But the disadvantage of live attenuated vaccines is also very obvious, that is, it is necessary to make a strain with just the right virulence, Long research and development time, and a very low probability of disease risk。
In terms of the current state of emergency of the epidemic, the time-consuming and labor-intensive conventional development route of live attenuated vaccines is currently too slow, and no potential candidate vaccine strains have yet been identified.
Inactivated vaccine, the beast is taxidermied
Corresponding to the sugar pill, the polio vaccine also has the option of completely inactivating the activity, which is the inactivated virus vaccine. This technology can also be used to produce a new crown vaccine.The specific method is to heat or use chemical reagents,Kill the virus and make it lose its pathogenicity, but because the protein on the surface of the virus still exists, injection into the human body can also trigger an immune response。
The virus here is like a beast that has been made into a specimen, but it is still morphologically intact. Rabies, flu, and hand, foot, and mouth disease vaccines are examples of this type of vaccine.The development of inactivated vaccines is relatively mature.As long as the suitable strains are screened out and can be produced on a large scale, the safety is generally better than that of live attenuated vaccines, In addition, vaccine effectiveness is not a problem as long as it does not destroy key parts of the virus's surface protein that can trigger an immune response.
Rapid scale-up of production may be a shortcoming of inactivated vaccines;At the same time, inactivated vaccines often require multiple vaccinations to generate antibodies with sufficient protection, and they are also insufficient when used as emergency vaccines. Inactivated vaccines and live attenuated vaccines have a common difficulty, that is, research and development and production involve virus culture, which requires relatively high biosafety requirements. risk.
At present, three domestic units have prepared inactivated vaccine samples and submitted them to the National Institute for Food and Drug Control for registration and inspection.,They are China Bio-Wuhan Institute of Biological Products/Wuhan Institute of Virology, Beijing Kexing Company, and Institute of Medical Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (Kunming Institute). Among them, the first two have obtained the approval notice of clinical trial from the State Food and Drug Administration, and the first inactivated vaccine has been inoculated with the first injection of Phase I/II clinical study in Wuzhi County, Henan Province on April 12 .
Since the production of inactivated vaccines requires high levels of biosafety, both Wuhan Institute of Biotechnology and Beijing Kexing have begun to build P3 (biosafety level 3) inactivated vaccine production workshops. Once the clinical research is completed and positive results are obtained, the first An inactivated vaccine can be produced and marketed at a time.
Recombinant protein vaccine, directly using the fur of the beast
If the first two are classic vaccine research and development methods, recombinant protein vaccines are a popular direction for vaccine research and development recently, because of their good safety and low cost.
This vaccine research and development method does not require isolation of virus strains at all. It only needs to express a large number of virus antigen proteins according to the sequence of the virus to make a vaccine. In other words, the vaccine will directly inject the protein that can trigger an immune response, as if directly injecting Use the fur of the beast. Hepatitis B, cervical cancer and hepatitis E vaccines are all works of this approach.The S protein on the surface of the new coronavirus can be used as the target protein for synthesis.
The biggest advantage of the recombinant protein vaccine technology route is high safety, because there is no need to directly manipulate the virus, and it is easy to scale up. However, this technique is not enough to express a protein sequence that is the same as that of a virus.The difficulty is that this protein also needs to be folded into the same structure as the virus. In response to this problem, scientists also have routines, such as allowing recombinant proteins to self-assemble into a virus-like particle, or using vaccine adjuvants to assist the effect of vaccines.
Pharmaceutical giant GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) has announced that it has jointly developed vaccines through this route with Chengdu Clover, Xiamen Wantai and another vaccine giant, Sanofi. In the cooperation mode, GSK provides the adjuvant system, and the partner provides the recombinant protein antigen. In addition, the cooperation team of Anhui Zhifeilong Kema/Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhejiang Pukang Biology/Institute of Virology of Hangzhou Medical College, and Novavax, a well-known American vaccine company, are also conducting such vaccine research.
If the new coronavirus really cannot disappear soon, perhaps the safety and accessibility of the recombinant protein technology route can really make the recombinant protein new crown vaccine a routine vaccine rather than an emergency vaccine.
Viral vector vaccine, "sheep in wolf's clothing"
The essence of this technology is "sheep in wolf's clothing".Find a way to place the protein on the surface of the new coronavirus on the surface of other viruses that are not powerful.. The "vector" here refers to this virus that has lost its power, that is, "sheep". The virus used as a sheep includes the adenovirus that has repeatedly appeared in the recent news.
At present, there are not many vector virus vaccines on the market, and none of them have been applied on a large scale. For example, the dengue vaccine using the attenuated yellow fever virus strain as the vector and the Ebola vaccine using the recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) as the vector ; A recombinant Ebola virus vaccine has also been developed in China, using adenovirus as a vector.
The advantage of viral vector vaccines is,Vehicles tend to induce strong immune responses, so additional adjuvants are usually not required. In addition, there are various inoculation methods, in addition to intramuscular inoculation, intranasal, intradermal or oral inoculation can also be used. The shortcoming is that some vector viruses may still be integrated into the human genome, which needs to be Careful evaluation during development. Moreover, if the carrier is a virus that can infect people, such as measles, influenza, and adenovirus, it may affect the protective effect of the vaccine because the vaccinated person already has antibodies.
Adenoviral vectors are one of the most commonly used viral vectors. After the outbreak of the new coronavirus, there are many research teams at home and abroad that use adenovirus as a carrier to develop targeted vaccines, such as Johnson & Johnson's Janssen Pharmaceuticals, the Chinese People's Liberation Army Academy of Military Sciences/CanSino team, Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology, Zhejiang Province Department of Science and Technology, Tsinghua University team, Tianjin University team, etc. Where,The adenovirus vector vaccine of the Academy of Military Sciences/CanSino team entered clinical phase I on March 16, Preliminary safety observation of vaccinated subjects has been completed;and entered clinical phase II on April 13 It is the first novel coronavirus vaccine in the world to enter clinical phase II research.。
Wuhan Bowo will cooperate with American biotechnology companies to develop a new crown vaccine using a replication-defective strain of vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA). The team of Yuan Guoyong of the University of Hong Kong is developing a new crown vaccine that can be used for nasal spray using the attenuated influenza strain as a carrier. The research and development of the Institut Pasteur in France to use the improved measles vaccine strain as a vector to express the antigenic gene of the new coronavirus is also in progress.
Nucleic acid vaccines (DNA vaccines/mRNA vaccines), the body's own synthetic beast fur
This method is different from the recombinant protein method, It is a direct injection of the nucleic acid encoding the virus antigen protein into the human body, and then the human body's cells synthesize the virus antigen protein by itself to generate an immune response span>. It also does not involve any virus operation, which is equivalent to directly exerting the effect of "fur", but this time even the fur is synthesized by the human body itself.
Nucleic acid vaccines are divided into DNA and mRNA.. Among them, DNA-injected vaccines have been used in the development of HIV, influenza virus, malaria, hepatitis B virus and other vaccines, and have entered the clinical trial stage. Some DNA vaccines have been approved for veterinary use, but no one has yet been approved for use with DNA vaccines. Most mRNA vaccines are only in the clinical stage, and they have considerable advantages in the field of cancer vaccines, influenza, HIV and other virus vaccines with high variability.
The advantage of the nucleic acid vaccine method is that the production process is relatively easy to standardize, and the raw materials of the vaccine can be synthesized by chemical synthesis, and the existing general equipment can be used. Scale production is relatively easy. These advantages can all play an advantage in emergencies like the new crown epidemic. The disadvantage of DNA vaccines is that this sequence may persist in the body for a long time, which may Integrated into the host chromosome, the protective effect may also be limited. mRNA vaccines do not enter the nucleus, and there is no risk of integrating the host genome. However, mRNA molecules also have shortcomings. They are not as stable as DNA, and the internal environment of the human body is complex. Whether the mRNA delivery system is effective is also a challenge.
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) is funding the development of INO-4800, a DNA vaccine against the novel coronavirus, by Inovio in the United States. The clinical trial database network (clinicaltrials.gov) shows that on April 6, Inovio has enrolled 40 healthy subjects to conduct a phase I clinical trial of INO-4800. Moderna's first batch of candidate mRNA vaccines, mRNA-1273, started clinical trials on March 16 stage study. On March 13, Fosun Pharma announced that it has paid US$85 million to obtain the exclusive development license of the mRNA vaccine from the German company BioNTech in the region. In addition, Germany's CureVac AG, Pfizer, domestic Tongji University Oriental Hospital, Shanghai Si Microbiology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai Lanque Bio and other teams are also using the mRNA platform to develop novel coronavirus vaccines. vaccine.
The vaccine development process is long and complex, and every step is full of uncertainty
Although the upgrading of technology is shortening the time for vaccine development, the vaccine development cycle is still very long after the indispensable steps of finding antigens, evaluating safety and selecting the best candidate vaccine, clinical development, registration approval, and production. Any step that doesn't go well can slow down or even end the entire R&D process.
Look for antigens
The search for antigens is a process of development and change.
Originally Pasteur invented the first generation of inactivated vaccines by heating and drying the spinal cords of animals that died of rabies. The inactivated rabies virus is an effective antigen. Later, live attenuated vaccines appeared using different methods to make the virus less virulent. For healthy people, a live attenuated virus that does not cause disease but can provide immune protection is an effective antigen.
For viruses that are not easy to culture in vitro, such as hepatitis B virus, the development of recombinant protein/genetic engineering technology allows the S protein of hepatitis B virus to be expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and can form a virus-like particle structure, becoming a safe and effective antigen. For this new coronavirus, in general,The main route to find antigens is still According to the nature of the virus itself, an antigen that is safe and can effectively stimulate the immune system is tailored for the candidate vaccine as the main active ingredient of the candidate vaccine. At the same time, the selection of antigens is also the design and verification process of technical routes that different research teams are good at.

Evaluating safety is not the best vaccine candidate
Vaccines are special drugs for healthy people, and their safety evaluation is a long process that goes through non-clinical trials, clinical trials and post-marketing evaluations.
If we only look at the preclinical research stage, we mainly use different animals to verify the long-term toxicity, acute toxicity, local irritation, allergy, and reproductive toxicity of the vaccine. (if women of childbearing age are considered for vaccination). The safety evaluation of vaccines usually requires special laboratories, which often take several months or longer. Therefore, vaccines developed using platform technologies such as mRNA, DNA, and viral vectors can not only shorten the development time, but also use similar early safety evaluation data to shorten part of the safety evaluation time.
The work of selecting candidate vaccines is actually the validation of preclinical studies on the effectiveness and protection of vaccines, often before the safety evaluation, or partially synchronously with the safety evaluation test.
Specific to the research and development of new crown vaccines: for recombinant protein vaccines, the expressed protein antigen must first be able to detect the combination with the virus serum of recovered new crown patients; make mRNA and DNA vaccines, the effective expression of the target protein in animals must be detected first; for recombinant virus vector vaccines, the effective packaging of the virus must be able to be effectively recognized by the virus serum of recovered new crown patients; finally, the inactivated vaccine of the new crown must be used. Similarly, the vaccines developed by the above-mentioned different routes, the serum after immunizing animals, must be able to neutralize different clinical isolates of the new coronavirus to be initially effective.
Finally, If these vaccines can protect the existing new crown model organisms from the disease after the new crown virus attack, there is no antibody-dependent disease enhancement effect (antibody - dependent enhancement, ADE) can be used as a truly effective vaccine candidate. The new crown vaccines currently approved for clinical use in China have all been verified by the above-mentioned series of model animal tests (ACE2 transgenic mice and rhesus monkeys). Moderna's mRNA vaccine has not undergone animal challenge virus tests, and has directly entered clinical phase I research, which makes many vaccine development professionals inevitably worry about the effectiveness of its clinical trials.
Clinical development (all phases of clinical trials)
Clinical trials of vaccines are generally divided into four phases.
Phase I trial focused on safety and clinical tolerability, the observation objects are generally healthy adults, usually in a small range, and 20 to 30 people are generally designed in China.
The purpose of the phase II trial is to observe or evaluate whether the vaccine can achieve the expected effect and general safety information in the target population. The minimum sample size required in China is 300 cases. Many vaccines that have been proven effective in animal experiments are often declared to have failed because phase II trials could not verify their effectiveness.
The purpose of the phase III trial is to comprehensively evaluate the protective effect and safety of the vaccine, which is the basis for obtaining registration and approval for marketing. Depending on the nature of the vaccine and the different diseases it prevents, the phase III trial designs of different vaccines vary greatly. For the rabies vaccine, a vaccine that has already been marketed, phase III trials are generally designed to involve hundreds or thousands of people. The HPV vaccine needs to be designed for phase III clinical trials of tens of thousands of subjects, and requires regular follow-up of up to 50 to 80 months. Even if some vaccines are developed in an abnormal sequence, the time required is 5 to 10 years, which often means that phase III clinical trials take a long time.
For the novel coronavirus pneumonia, a new and sudden infectious disease, it may be necessary to conduct a phase III clinical trial in its endemic area to observe the difference in viral infection between the control group and the experimental group. In view of the current development and control of the domestic new crown pneumonia epidemic, it is very unlikely that the new crown vaccine will undergo phase III clinical trials in China. At that time, it may only be possible to select subjects in foreign regions where the new crown virus is endemic for Phase III clinical research. If the foreign epidemic situation is also well controlled and there is no suitable Phase III clinical research population, the new crown vaccine that has completed the Phase II clinical study can also be used as a national reserve vaccine for use in emergencies in the future.
Phase IV clinical trials are a comprehensive evaluation of the safety and efficacy of the vaccine in the actual application population after the vaccine is registered and marketed.
my country's vaccine clinical trials are basically carried out by the vaccine research and development or production enterprises as sponsors, and the provincial CDCs as researchers to implement the specific implementation. This is different from common drugs that are often clinically researched in hospitals.
Registration approval and production of the first batch of vaccines
After completing preclinical research and preclinical safety evaluation, vaccine companies submit relevant materials to apply for clinical trials; after obtaining approval, they will conduct clinical research in various phases, and only after achieving expected clinical results and submission of reports, can they be approved for marketing.
After that, vaccine companies generally need to continuously produce three batches of qualified vaccines under the supervision of the drug regulatory agency before they can obtain a vaccine production license to ensure that the production process of the company is stable.
Each batch of vaccines that are finally produced on the market, as well as the clinical vaccines manufactured before, must pass both the enterprise self-inspection and the verification of the China National Institute for Food and Drug Control before they can be released. The national inspection for the release of marketed drugs is called lot release.
Production (Quality Control)
The quality control of vaccines can be roughly divided into three stages. The first is the quality control of the raw materials for vaccine production, the second is the quality control of the production process, and the third is the inspection and testing of the intermediate and final products of vaccine production. . These three parts are important conditions for ensuring the quality and safety of vaccines, and they are indispensable.
All raw materials used in vaccine production must have reliable sources. In addition to the most important sources of bacterial and viral species, cell matrices and other antigenic components, other materials such as culture medium, buffer solutions, and utensils should be strictly managed. Especially for animal-derived raw materials, if it is clearly stipulated in China that bovine-derived raw materials should be excluded from the control of mad cow disease epidemic areas.
The quality of vaccine products is determined by a series of factors in the entire process from raw material input to product delivery. Therefore, the quality of vaccines is produced, not verified. Verification only objectively reflects the quality level of the supervised vaccine.
The vaccine production process requires implementation of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice for Drugs) and "China relevant provisions of the Pharmacopoeia. The GMP of vaccines is a huge and complex content, so I won't go into details here. The general principle is that while the staff in the production workshop matches the requirements for vaccine production, the entire production process conforms to the approved production process, operates in strict accordance with the standard operating procedures, and controls every link of the entire production process to the greatest extent possible. Meets all quality requirements.
Finally, it should be emphasized that vaccines are special drugs for healthy people, and each batch of products requires batch release inspection, which is higher than that of ordinary drugs.

How far is the new crown vaccine
Following the traditional process, it may take 5 to 10 years for a vaccine to go from development to market. This speed is obviously unacceptable to people today.
Under the current emergency situation, it is not impossible to find a "shortcut" for vaccine research and development in terms of policy. Saturated scientific research investment, all-round resource inclination, simultaneous development of multiple lines of work, day and night efforts of scientific researchers, and continuous rolling review and approval by review institutions are the basis for the rapid development of new crown vaccines.
Nucleic acid vaccines and viral vector vaccines are indeed relatively fast-moving technical routes at present. However, even if the whole process is completed at the fastest speed, it will take more than a year. In view of the current severe situation of the new coronavirus raging around the world,Currently some companies are trying to pass phase I clinical trials that are relatively complex and have more subjects (or seamless design after combined Phase I and II clinical trials),At the same time as the safety data of the candidate vaccine, the dosage, dosage schedule and its effectiveness should be clarified as soon as possible. In this way, it may be possible to apply for exemption from Phase II clinical trials and quickly enter Phase III clinical trials.
In my opinion, given the urgency of the current epidemic, If a vaccine is proven to be effective through Phase I and Phase II clinical trials(On the premise of ensuring security),Maybe consider carrying out a relatively large-scale single arm in an emergency (no control group, all test vaccines)III Phase clinical design. First give medical staff, epidemic prevention personnel and other susceptible people the greatest possible protection, and then compare and analyze the infection data of people in unvaccinated areas , to finally determine the actual results of Phase III clinical trials.
As an emergency use, the speed advantage of the early development of nucleic acid vaccines and viral vector vaccines allows them to enter the runway first. However, as a traditional technical route with a relatively slow research and development speed, inactivated, attenuated and recombinant protein vaccines can also be adjusted in the follow-up depending on the development of the epidemic situation. Maybe in the future, the global demand for vaccines will be astronomical; it also needs to be safer and more effective , Vaccines that are easy to produce, transport and vaccinate will also have higher requirements on the production cost and mass production capacity of vaccines. Vaccines with different technical routes may stand out in different stages of the epidemic in the future。
During the SARS epidemic in 2003, a number of research teams conducted research and development of SARS vaccines with various technical routes. However, because the epidemic was quickly brought under control, when the research phase of the relevant vaccines advanced to clinical trials, there were no subjects at all. The situation has made relevant research and development become "the art of slaying the dragon", and in the end, it can only be left to nothing.
If the new crown epidemic can be successfully controlled after the vaccine is developed, we should also pay attention to the experience and lessons brought by this epidemic. While paying attention to the establishment of the public health defense system and emergency response system, we should do a good job in the research and development platform of general coronavirus emergency vaccine, general respiratory virus emergency vaccine research and development platform and even general infectious disease pathogen emergency vaccine research and development platform, including its related emergency clinical programs and The emergency use plan can really avoid the situation that vaccines are not urgent in the face of the epidemic.


