Research Background
On April 28, 2020, the results of the latest epidemiological survey led by Professor Teng Weiping was published online in BMJ magazine(WeipingTeng, BMJ. 2020; 369: m997.)。
this time flowkey numberAccording toThyroid disorders, Iodinestatus and Diabetes Epidemiological survey, TIDE study). Using multiple Stage stratified sampling method, nationally representative sampling of people over 18 years old, with a total sample of 75,880 people, covering 31 provinces across the country.
Research result
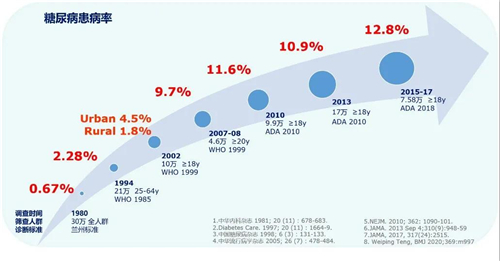
1. The prevalence of diabetes among adults in China keeps increasing
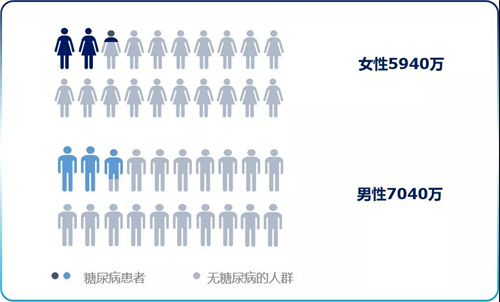
According to ADA criteria, the prevalence of diabetes in Chinese adults is 12.8%, the proportion of prediabetes is 35.2%, and the prevalence of diabetes is 35.2%. The total number of patients is 129.8 million, 59.4 million female patients and 7040 male patients million people.
2. Risk factors for diabetes
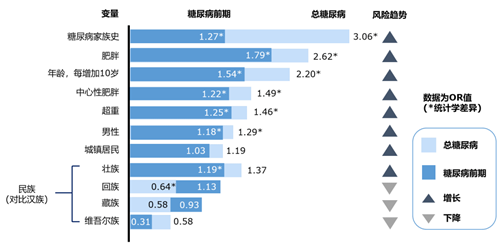
Family history of diabetes, advanced age, male gender, overweight, Obesity and central obesity are major risk factors for diabetes .
3. Regional differences between diabetes and prediabetes
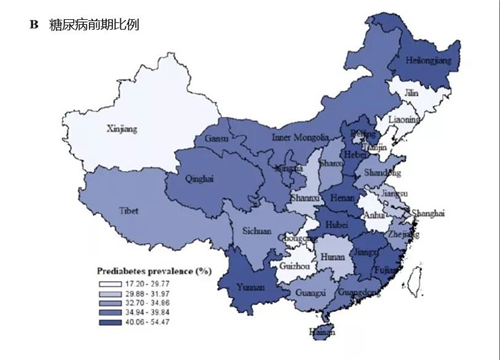
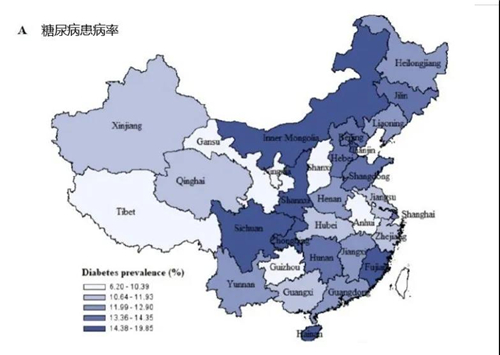
Among the 31 provinces, the proportions of diabetes and prediabetes varied widely. The prevalence of diabetes: the highest in Inner Mongolia (19.9%) and the lowest in Guizhou (6.2%);The proportion of prediabetes: the highest in Yunnan (54.5%) and the lowest in Anhui (17.2%).
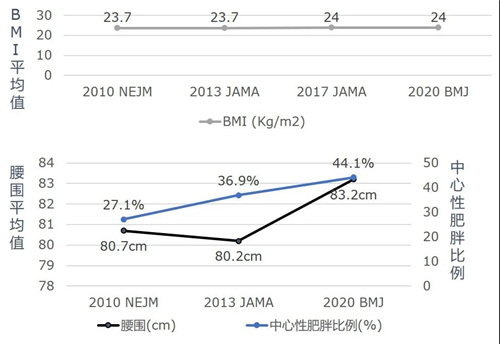
4. BMI and waist circumference significantly affect diabetes prevalence
The authors defined overweight, obesity, and central obesity by body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference, respectively (Figure 7), and found:As BMI increased, both the prevalence of diabetes and the proportion of prediabetes tended to increase;The prevalence of diabetes and the proportion of prediabetes in the centrally obese population were also significantly higher than those in the normal body size population;In 10 years, the average BMI did not change significantly, but the prevalence of central obesity showed an increasing trend.